The Deployment Nightmare
A startup built a web app that worked perfectly on the developer’s laptop. But when deployed on a server, it crashed due to missing dependencies.
The problem? Inconsistent environments between development and production.
The solution? Containerization and orchestration, ensuring apps run consistently, efficiently, and at scale.
What is Containerization?
Containerization packages applications and their dependencies into a lightweight, portable unit that runs consistently across environments.
Example: A Python app inside a container will run the same way on a developer’s machine, staging, and production.
Key Benefits:
Portability: Runs anywhere without compatibility issues.
Lightweight: Uses fewer resources than virtual machines.
Faster Deployment: Eliminates manual configuration.

Docker – The Standard for Containerization
Docker is the most widely used tool for creating and managing containers.
Key Features:
Docker Images: Prebuilt environments for applications.
Docker Containers: Isolated runtime environments.
Docker Compose: Manages multi-container applications.
Example:
# Dockerfile for a Node.js app
FROM node:18
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN npm install
CMD ["node", "server.js"]Use Case: Spotify uses Docker to deploy microservices independently.
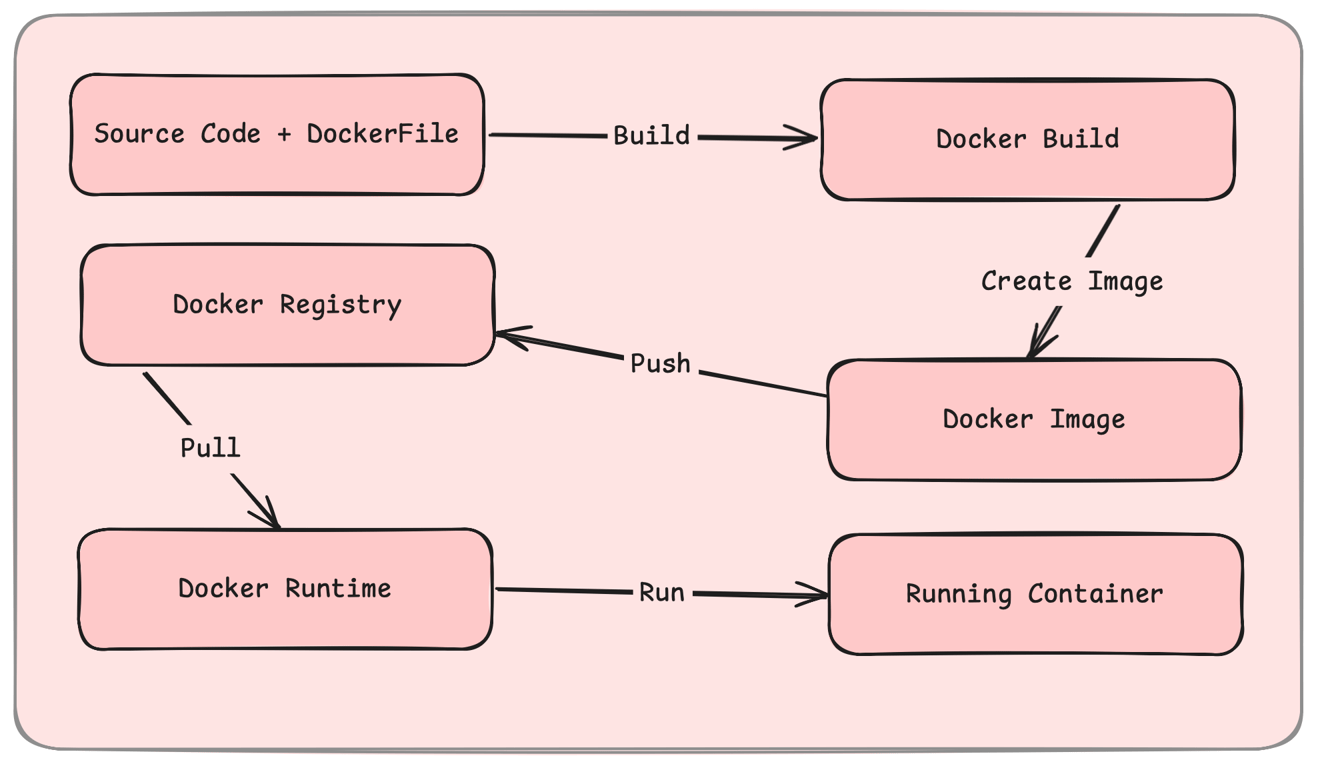
What is Container Orchestration?
Orchestration automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containers across multiple machines.
Key Features:
Auto-Scaling: Adjusts resources based on traffic.
Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across containers.
Self-Healing: Restarts failed containers automatically.
Kubernetes – The Industry Standard for Orchestration
Kubernetes (K8s) is a container orchestration platform that automates the deployment and scaling of containers.
Key Components:
Pods: The smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes.
Nodes: Machines that run containers.
Services: Expose containers to the network.
Example: Netflix uses Kubernetes to scale microservices dynamically.
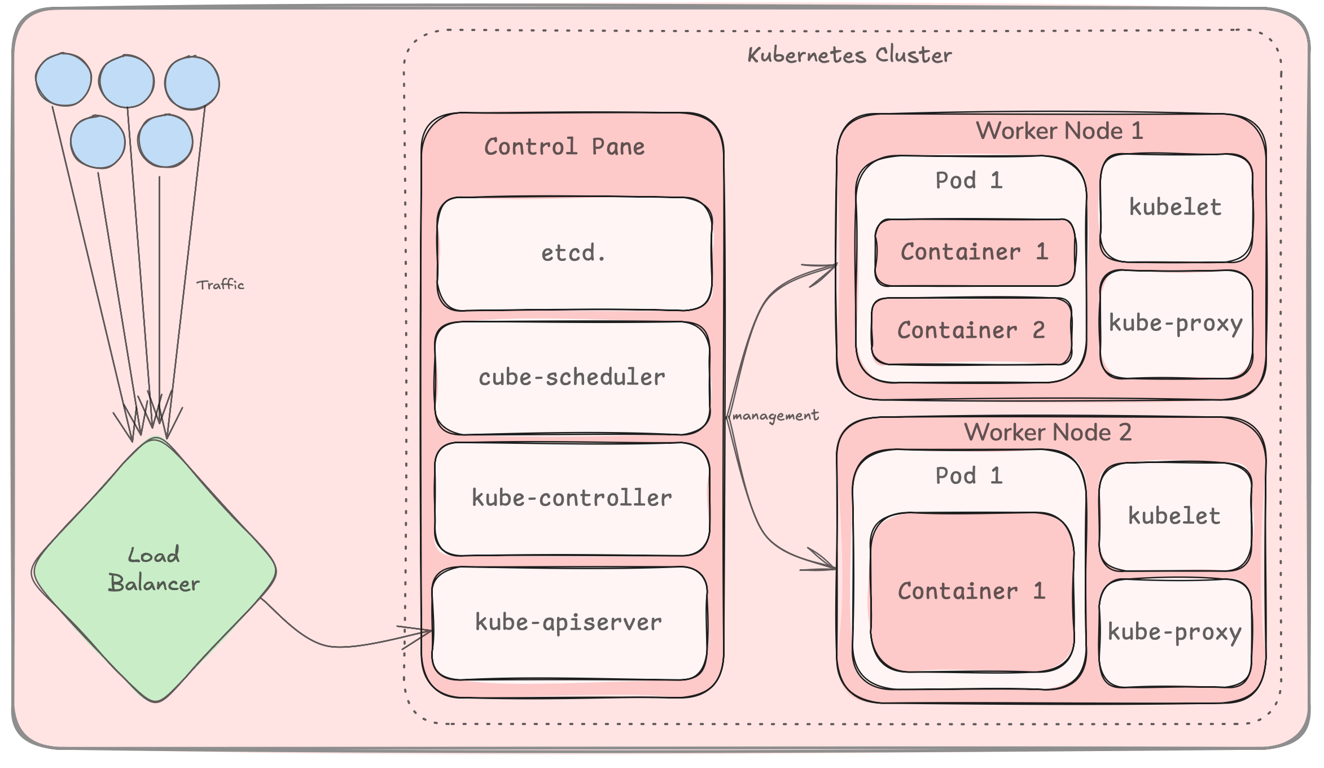
AWS ECS – Fully Managed Container Orchestration
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) provides a managed orchestration solution for AWS users.
Key Features:
Deep AWS integration (S3, RDS, IAM).
Supports both EC2 and Fargate (serverless containers).
Simplified container management compared to Kubernetes.
Use Case: Airbnb uses ECS to deploy and scale its microservices automatically.
Service Mesh – Managing Microservices Traffic
A Service Mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer for handling service-to-service communication.
Key Features:
Traffic Control: Routes requests between microservices.
Security: Encrypts communication (mTLS).
Observability: Monitors and traces requests.
Popular Service Meshes:
Istio – Works with Kubernetes for advanced traffic management.
Linkerd – Lightweight and optimized for simplicity.
Example: Twitter uses a service mesh to ensure low-latency API communication.
Choosing the Right Tool
Feature
Docker
Kubernetes
ECS
Service Mesh
Containerization
✔
✖
✖
✖
Orchestration
✖
✔
✔
✖
Auto-Scaling
✖
✔
✔
✖
Traffic Management
✖
✖
✖
✔
Real-World Use Cases
1. E-Commerce Websites
Docker containers package checkout and payment services.
Kubernetes scales microservices based on demand.
Istio Service Mesh ensures secure API communication.
2. Streaming Platforms
ECS manages video transcoding services.
Service Mesh optimizes load balancing for video delivery.
3. FinTech Applications
Docker ensures security compliance in banking apps.
Kubernetes handles real-time transaction processing.
Conclusion
Containerization and orchestration simplify application deployment, scaling, and management.
Docker packages applications into portable containers.
Kubernetes and ECS automate deployment and scaling.
Service Mesh ensures secure and efficient microservices communication.
Next, we’ll explore Serverless Architectures – AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, FaaS Concepts.


